
Characteristics of the disease
According to medical statistics, more than 30% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis. And every year the patients are younger. But compared to cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis, thoracic osteochondrosis is much less common.
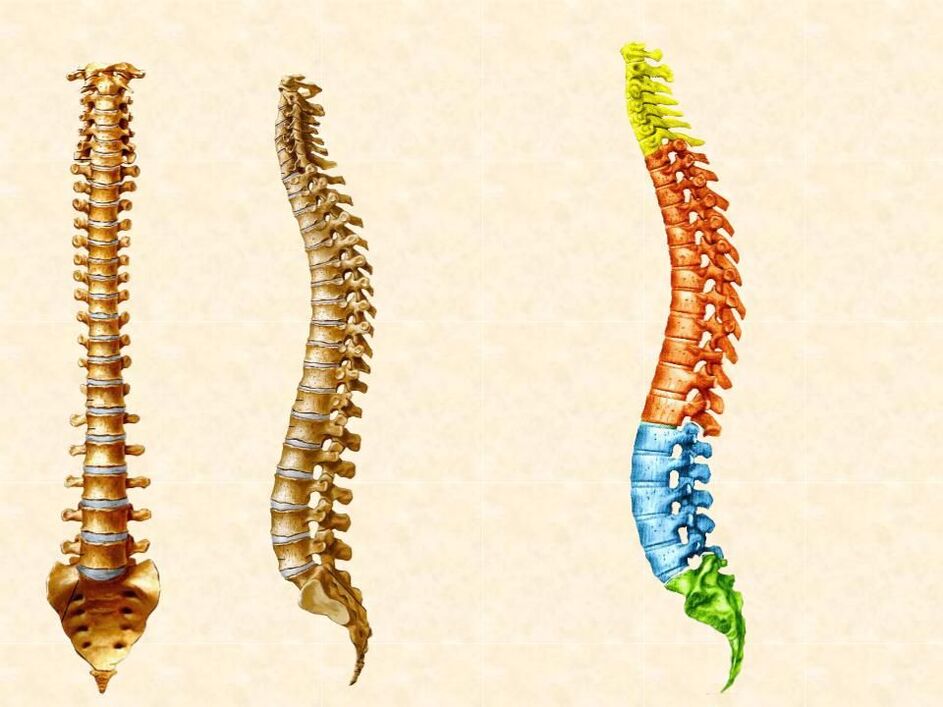
- it has a natural bend, thanks to which part of the load from straight walking is removed from it;
- the other part falls on the ribs and sternum, which play the role of a physiological framework;
- it is the longest section of the spine (12 vertebrae), but the spinal canal is the narrowest;
- the thoracic vertebrae are small but equipped with long spinous processes;
- inactive.
If the intervertebral disc deformation appears in the chest region, it gradually disappears. But it manifests painfully.
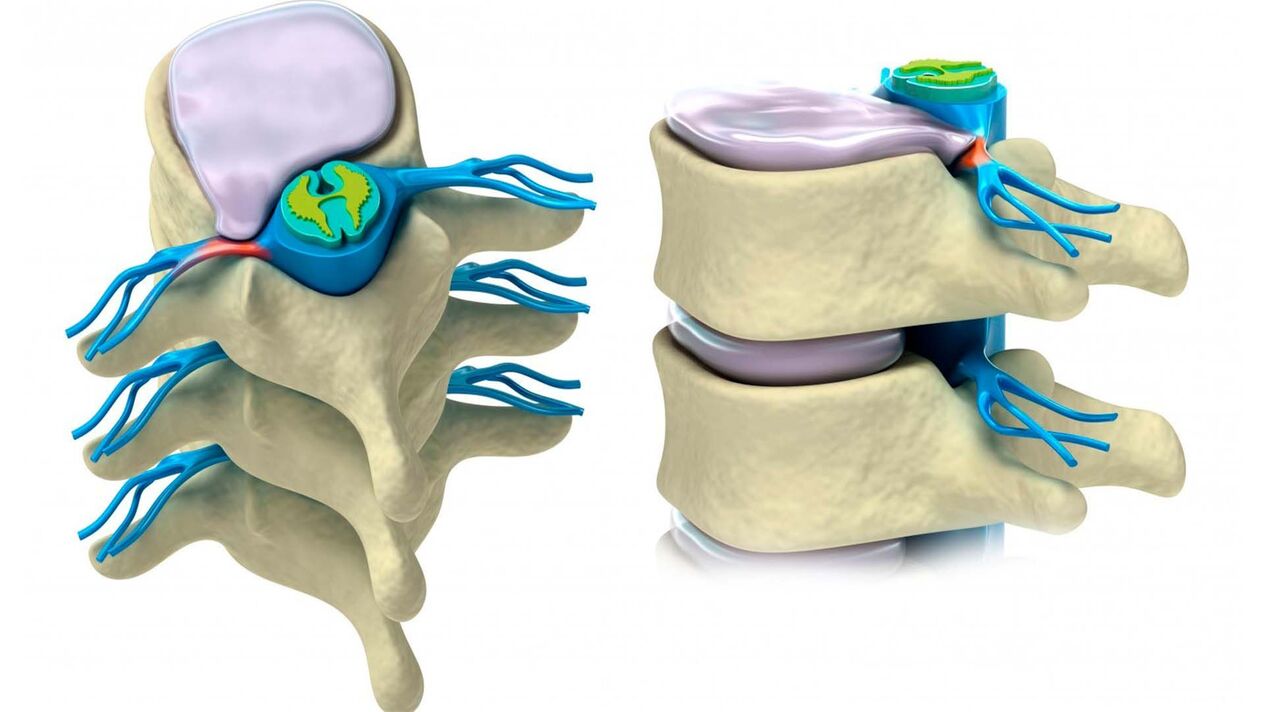
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
How clearly the disease manifests itself depends on the stage of the disease, lifestyle and age.
- Pain. It is felt in the upper part of the back, between the shoulder blades, and surrounds the intercostal spaces with neuralgia. It gets worse with coughing, deep breathing and turning the body. Because there are many nerve fibers in the chest, chest pain (dorsago) appears, as if it were a heart attack.
- Radiculitis. In addition to pain, there is also a loss of sensitivity. Typically, the limbs, upper abdomen and the area below the collarbone become numb.
- Paresthesia. You have a feeling of goosebumps crawling all over your body.
- Cardiac syndrome. Severe heart pain persists, which does not go away even after taking the medicine.
- Pulmonary syndrome. It manifests itself in suffocation and congestion of the lungs.
- Abdominal syndrome. It is characterized by persistent pain in the digestive organs.
- Muscle tension. It occurs reflexively in the upper back and chest.
In men and women, the clinical picture is approximately the same. But the signs of thoracic osteochondrosis in women usually appear at the beginning of menopause. Before this, the spine is protected by estrogens.
In men, the complications of the disease can affect potency.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis are much more disturbing at night than during the day. They become stronger as a result of hypothermia, exercise and stress. It is believed that women suffer from spinal pain more severely.
Localization of the pain syndrome
The diagnosis of the disease is complicated by the fact that the symptoms are similar to other diseases: heart attack, angina pectoris and gastrointestinal disorders.
- In the case of thoracic osteochondrosis, the symptoms associated with a feeling of heartache appear when the first and sixth thoracic nerves are affected. In women, the mammary glands may hurt.
- If the 6-9. thoracic nerve is affected, pain occurs in the stomach. The sensations are the same as in colitis and gastritis. The presence of a foreign body in the esophagus can be felt.
- In the small intestine, kidneys and genitals, if pathological processes affect the 11th and 12th discs.
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, the orthopedic surgeon prescribes an examination for the patient.
X-rays, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, EKG and, for women, mammography.
The results help determine the stage of the disease and treatment options.
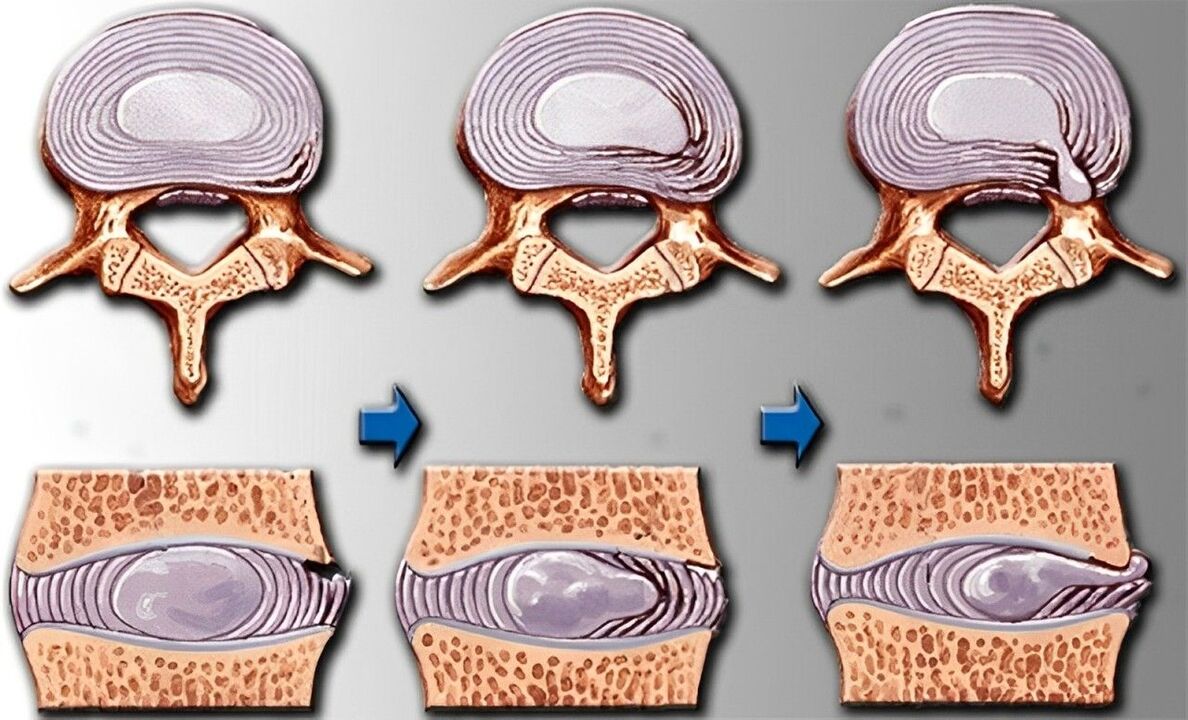
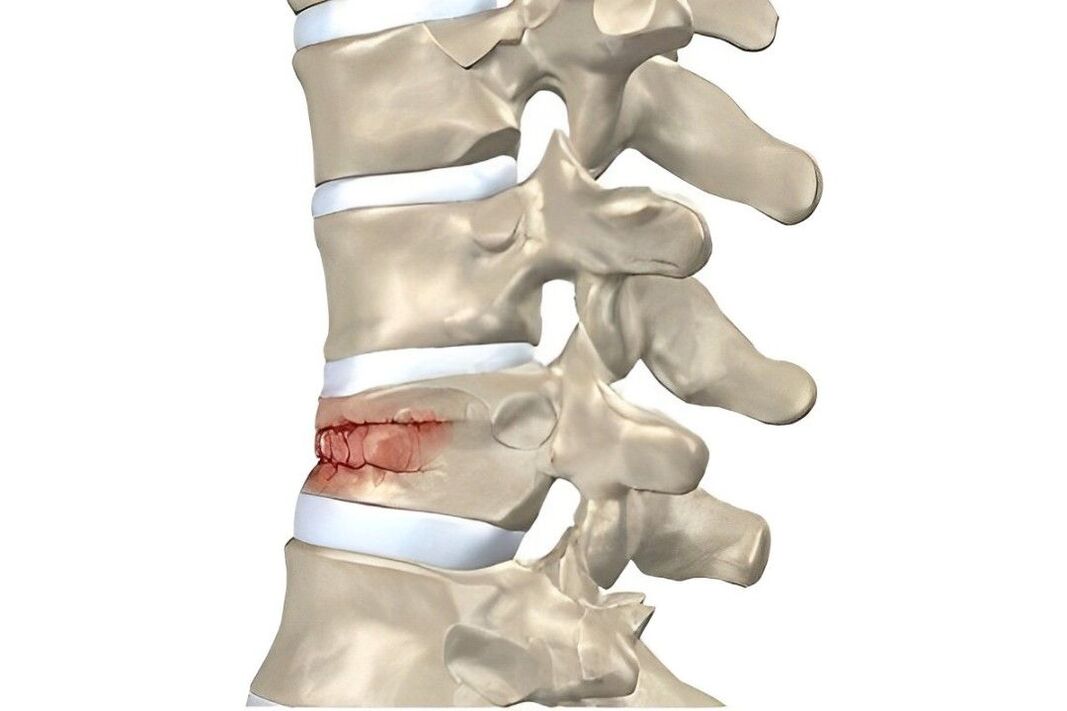
Stages of the disease
| Stage | Changes | Symptoms |
| First | Dehydration of the discs, which causes a loss of elasticity. Their height decreases, but their width increases - the intervertebral disc gradually flattens. | The pain appears directly in the damaged ring. This can be a drag or shoot. |
| Second | The annulus fibrosus begins to disintegrate. The nerve roots are compressed, causing pain. | Pain occurs during movement. If you maintain the pose for a long time, you will feel discomfort. |
| Third | The annulus fibrosus tears, resulting in a herniated disc. Scoliosis or pathological kyphosis develops. | Pain occurs during movement. If you maintain the pose for a long time, you will feel discomfort. |
| Fourth | The vertebrae rub against each other, which causes displacement of the intervertebral joints. The tissue surrounding the vertebrae becomes inflamed. Cartilage tissue is replaced by bone tissue, which reduces motor functions. Fibrosis appears. | Pain occurs during movement. If you maintain the pose for a long time, you will feel discomfort. |
Phases of exacerbation and remission can be observed. The latter is often observed in stage 4.
Degrees of the disease
This is a more modern classification of symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, which is used by specialists.
| degrees | Changes and symptoms |
| First | Intervertebral disc rupture caused by sudden movement or overexertion. Sharp pain, similar to the passage of electric current along the spinal column. Muscle strain. |
| Second | It is characterized by instability of the spinal column. Pain when moving. Protrusion. |
| Third | The pain becomes constant. Loss of sensation. Change in gait. Severe headache. Difficulty breathing. Tachycardia. |
| Fourth | The spine is unstable: the vertebrae slip and twist. Osteophytes grow, pinching spinal nerves and putting pressure on the spinal cord. |
Osteochondrosis of the chest can cause serious diseases that will be difficult to cure.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
The symptoms of women practically do not differ from the clinical picture of men. The main difference in this case is that in the female half of humanity, osteochondrosis develops at an older age. The female body has a peculiarity - estrogens effectively protect the intervertebral discs from destruction, therefore, the signs of osteochondrosis in women most often appear during menopause or hormonal imbalance. In addition, as already mentioned, the signs of osteochondrosis of the chest can be similar to the symptoms of dangerous diseases of the mammary glands.
Therefore, women should undergo tests such as mammography to clarify the diagnosis.
Osteochondrosis of the chest in women can manifest itself in different ways. The clinical picture depends on the age, the stage of the pathology, and which vertebra is affected and to what extent. One of the signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine in women is a burning sensation and itching between the shoulder blades.
- Dorsago ("chest lumbago", "stabbing pain") is a sudden, strong, sharp pain in the chest (between the shoulder blades), which most often occurs after a long stay in the same uncomfortable position. With chest lumbago, the muscles tense up sharply and strongly - the person feels that breathing has become difficult. The pain below the lower back can be aggravated when you rotate your upper body.
- Thoracalgia is chronic mild pain in the sternum. Thoracalgia can manifest itself not only with osteochondrosis, but also with diseases of the internal organs located in this area (lungs, heart, stomach). The main difference between such pain in osteochondrosis is its superficiality and segmental manifestation along the intercostal spaces. Thoracalgia associated with osteochondrosis is aggravated by movements and deep breathing, and subsides with rest.
- numbness, goosebumps in some areas of the skin;
- burning sensation, itching between the shoulder blades;
- cold feeling in the legs;
- pain in the pharynx and esophagus;
- disorders of the stomach and intestines.
Treatment of pathology in women
It is practically impossible to completely get rid of already advanced thoracic osteochondrosis, but with the tools and methods of modern medicine, it is completely possible to slow down or even stop the development of the pathological degenerative-dystrophic process in the tissues of the spinal movement segments. . The optimal therapeutic effect can only be achieved with an integrated approach to the treatment of this pathology, with drug treatment, various physiotherapy techniques and targeted exercise therapy techniques (physiotherapy).
Symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are not too different from those of men. In the acute period of osteochondrosis of the thoracic segment of the spine, the patient needs intensive exacerbation treatment, during which various drugs and physical procedures are used to help eliminate primarily the pain syndrome and, in parallel, other negative manifestations. about the disease.
During remission, the patient must be prescribed maintenance treatment, primarily based on the restoration of the osteochondral structure and physical therapy. In particularly severe cases, surgical intervention is sometimes resorted to in order to stabilize the position of the spinal column.
Sensation in women with osteochondrosis
- Painful manifestations in the area of the heart. In this case, the symptoms are more similar to heart diseases, such as a heart attack or angina. The pain is dull or aching and may last for months. However, vascular drugs do not improve, and ECG results show no abnormalities.
- Unpleasant feeling in the mammary glands. It manifests itself most often in women, characterized by nagging painful sensations. It can often be confused with diseases of the mammary glands. In this case, a more detailed diagnosis is required.
- Just cramps and pain in the abdominal cavity. It is characterized by signs characteristic of various pathological processes in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, which are often mistaken for gastritis, ulcers or cholecystitis. It increases with physical movements.
Experts have also identified two signs of thoracic osteochondrosis, which, if detected, can immediately indicate the development of the disease - the so-called dorsago and dorsalgia.
Complications of the disease
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a painful disease that greatly reduces the patient's quality of life.
Osteochondrosis often affects several departments gradually or simultaneously.
- for cardiovascular disorders;
- vegetative system;
- digestive;
- respiratory;
- faint;
- dizziness;
- panic attacks and fear that occur with rapid heartbeat and choking;
- chronic fatigue;
- Shingles.
Therefore, the treatment of the disease must be comprehensive, aimed at eliminating all symptoms. In case of early and correct diagnosis, the treatment is associated with a favorable prognosis.






















